Shading hypotheses make a consistent structure for shading.
For instance, in the event that we have a combination of leafy foods, we can arrange them by shading and place them on a circle that demonstrates the hues in connection with each other.
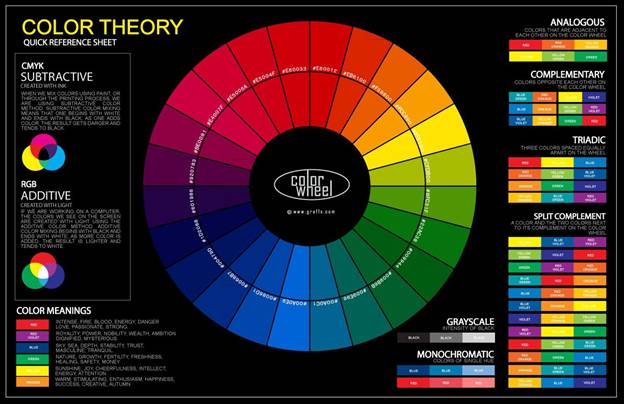
The Colour Wheel
As per the traditional art from the field of design, a color circle is based on red, yellow and blue.
The father of science, Sir Isaac Newton is the first person who developed the first circular diagram of colors in the year 1666.
From that time then, artists along with scientists have learned as well as designed plentiful variations of this concept.
Contrasts of feeling about the legitimacy of one arrangement over another keep on provoking open deliberation.
In actuality, any shading circle or colour wheel which exhibits a consistently orchestrated succession of unadulterated tints has justified.
Primary Essential Colours: Red, yellow and blue
In customary shading hypothesis, essential hues are the 3 shade hues that can’t be blended or shaped by any mix of different hues. Every other shading is gotten from these 3 hues of color.
Secondary Colours: Green, orange and purple
These are the hues framed by blending the essential hues.
Tertiary Colours: These are the hues framed by blending an essential and an auxiliary shading.
Colour Wheel Theory with Animation Kolkata
That is the reason the tint is a two-word name, for example, blue-green, red-violet, and yellow-orange.
What is Colour Harmony?
Now you might get confused that how harmony is related to colors.
Lets’ make it clear to you.
The phrase ‘Harmony‘ is referred to as a fascinating arrangement of portions, may it be color or poetry.
In visual encounters, concordance is something that is satisfying to the eye.
It connects with the watcher and it makes an inward feeling of the request, an adjust in the visual experience.
When something isn’t agreeable, it’s either exhausting or riotous.
At one outrageous is a visual affair that is bland to the point that the watcher isn’t locked in. The human cerebrum will dismiss under-fortifying data.
At the other extraordinary is a visual affair that is so overcompensated, so disordered that the watcher can’t remain to take a gander at it.
The human cerebrum rejects what it can’t sort out, what it can’t get it.
The visual undertaking requires that we introduce a coherent structure.
Shading harmony or colour harmony conveys visual intrigue and a feeling of a request.
In outline, outrageous solidarity prompts under-incitement, extraordinary unpredictability prompts over-incitement.
Amicability is a dynamic harmony.
Formulas of Colour Harmony
In the field of color harmony, there is the huge type of colour theories.
Present below are the descriptions of color harmony:
Colour Scheme based on Analogous colors
Analogous color is defined as any three colors which are cheek to cheek on a 12-part color wheel that comprises of yellow-green, yellow and yellow-orange.
But generally what happens is one of the colors prevails.
Colour Scheme based on Complementary colors
Reciprocal hues or complementary colours are any two hues which are straightforwardly inverse each other, for example, red and green and red-purple and yellow-green.
In the delineation above, there are a few varieties of yellow-green in the leaves and a few varieties of red-purple in the orchid.
These restricting hues make the greatest complexity and most extreme security.
Colour Scheme based on Nature
Nature is that part of the color that brings in an absolute departure point for the purpose of color harmony.
In some cases, red-yellow and green color makes a perfect combo in natural depictions.
Colour Context
Colour Context is how shading carries on in connection with different hues and shapes is an unpredictable region of shading hypothesis.
Think about the complex impacts of various shading foundations for a similar red square.
Red is one of the brightest colors and it shows much credible as well as radiant against a black background.
However, it is sometimes duller against a white background.
On the contrary to orange color, the red color seems unresponsive and in addition, it is also vital to mention that red, on contrary to green color exhibits brilliance.
For the red color, the background of black color appears more vibrant and large as compared to the other background colors.
So it can be concluded that a color wheel is effective in the visual representation of colors assembled as per their chromatic relationship.
A color wheel can be well analyzed and studied by means of positioning primary hues that is equivalent to one another and then generate a bridge or gap between the primaries utilizing secondary and tertiary colors.
Active and Passive Colours
The color wheel can be categorized into ranges and this two are visually active or passive.
When the active colors are placed against passive hues, active colors will seem to advance.
Propelling hues and tints are regularly thought to have less visual weight than the subsiding tones.
Regularly warm, soaked, light esteem tones are “dynamic” and outwardly progress.
Cool, low immersed, dim esteem tints are “latent” and outwardly subside.
Tints or tones with a low immersion seem lighter than shades or very soaked hues.
A few hues remain outwardly nonpartisan or apathetic.
Colour Relationships
Colour Relationships can be demonstrated as a color wheel or a color triangle.
Understanding colour relationship is it self a huge study.
The color triangle is the best way to make one get a better understanding of the color wheel theory.
The Colour Triangle of a Painter
It comprises of colors that people most frequently discussed in the art class concentrating on the three primary colors such as red, blue and yellow.
The Colour Triangle of a Printer
Colour Wheel Theory with Animation Kolkata
It is known for its set of colors utilized in the printing process.
In this case, the primary hues are magenta, cyan, and yellow.
The Nine-part harmonic triangle of Goethe
This part starts with the printer’s primary hues along with the secondary formations hues (painter’s hues) and the final tertiaries formed areas equivalent to dark neutral hues.
This blog post is presented by the global leader of Animation–Visual Effects–Web–Gaming, MAAC Kolkata with a view to educating the leaders about the different color wheel theories that are popular in the field of hues.
For instance, in the event that we have a combination of leafy foods, we can arrange them by shading and place them on a circle that demonstrates the hues in connection with each other.
The Colour Wheel
As per the traditional art from the field of design, a color circle is based on red, yellow and blue.
The father of science, Sir Isaac Newton is the first person who developed the first circular diagram of colors in the year 1666.
From that time then, artists along with scientists have learned as well as designed plentiful variations of this concept.
Contrasts of feeling about the legitimacy of one arrangement over another keep on provoking open deliberation.
In actuality, any shading circle or colour wheel which exhibits a consistently orchestrated succession of unadulterated tints has justified.
Primary Essential Colours: Red, yellow and blue
In customary shading hypothesis, essential hues are the 3 shade hues that can’t be blended or shaped by any mix of different hues. Every other shading is gotten from these 3 hues of color.
Secondary Colours: Green, orange and purple
These are the hues framed by blending the essential hues.
Tertiary Colours: These are the hues framed by blending an essential and an auxiliary shading.
Colour Wheel Theory with Animation Kolkata
That is the reason the tint is a two-word name, for example, blue-green, red-violet, and yellow-orange.
What is Colour Harmony?
Now you might get confused that how harmony is related to colors.
Lets’ make it clear to you.
The phrase ‘Harmony‘ is referred to as a fascinating arrangement of portions, may it be color or poetry.
In visual encounters, concordance is something that is satisfying to the eye.
It connects with the watcher and it makes an inward feeling of the request, an adjust in the visual experience.
When something isn’t agreeable, it’s either exhausting or riotous.
At one outrageous is a visual affair that is bland to the point that the watcher isn’t locked in. The human cerebrum will dismiss under-fortifying data.
At the other extraordinary is a visual affair that is so overcompensated, so disordered that the watcher can’t remain to take a gander at it.
The human cerebrum rejects what it can’t sort out, what it can’t get it.
The visual undertaking requires that we introduce a coherent structure.
Shading harmony or colour harmony conveys visual intrigue and a feeling of a request.
In outline, outrageous solidarity prompts under-incitement, extraordinary unpredictability prompts over-incitement.
Amicability is a dynamic harmony.
Formulas of Colour Harmony
In the field of color harmony, there is the huge type of colour theories.
Present below are the descriptions of color harmony:
Colour Scheme based on Analogous colors
Analogous color is defined as any three colors which are cheek to cheek on a 12-part color wheel that comprises of yellow-green, yellow and yellow-orange.
But generally what happens is one of the colors prevails.
Colour Scheme based on Complementary colors
Reciprocal hues or complementary colours are any two hues which are straightforwardly inverse each other, for example, red and green and red-purple and yellow-green.
In the delineation above, there are a few varieties of yellow-green in the leaves and a few varieties of red-purple in the orchid.
These restricting hues make the greatest complexity and most extreme security.
Colour Scheme based on Nature
Nature is that part of the color that brings in an absolute departure point for the purpose of color harmony.
In some cases, red-yellow and green color makes a perfect combo in natural depictions.
Colour Context
Colour Context is how shading carries on in connection with different hues and shapes is an unpredictable region of shading hypothesis.
Think about the complex impacts of various shading foundations for a similar red square.
Red is one of the brightest colors and it shows much credible as well as radiant against a black background.
However, it is sometimes duller against a white background.
On the contrary to orange color, the red color seems unresponsive and in addition, it is also vital to mention that red, on contrary to green color exhibits brilliance.
For the red color, the background of black color appears more vibrant and large as compared to the other background colors.
So it can be concluded that a color wheel is effective in the visual representation of colors assembled as per their chromatic relationship.
A color wheel can be well analyzed and studied by means of positioning primary hues that is equivalent to one another and then generate a bridge or gap between the primaries utilizing secondary and tertiary colors.
Active and Passive Colours
The color wheel can be categorized into ranges and this two are visually active or passive.
When the active colors are placed against passive hues, active colors will seem to advance.
Propelling hues and tints are regularly thought to have less visual weight than the subsiding tones.
Regularly warm, soaked, light esteem tones are “dynamic” and outwardly progress.
Cool, low immersed, dim esteem tints are “latent” and outwardly subside.
Tints or tones with a low immersion seem lighter than shades or very soaked hues.
A few hues remain outwardly nonpartisan or apathetic.
Colour Relationships
Colour Relationships can be demonstrated as a color wheel or a color triangle.
Understanding colour relationship is it self a huge study.
The color triangle is the best way to make one get a better understanding of the color wheel theory.
The Colour Triangle of a Painter
It comprises of colors that people most frequently discussed in the art class concentrating on the three primary colors such as red, blue and yellow.
The Colour Triangle of a Printer
Colour Wheel Theory with Animation Kolkata
It is known for its set of colors utilized in the printing process.
In this case, the primary hues are magenta, cyan, and yellow.
The Nine-part harmonic triangle of Goethe
This part starts with the printer’s primary hues along with the secondary formations hues (painter’s hues) and the final tertiaries formed areas equivalent to dark neutral hues.
This blog post is presented by the global leader of Animation–Visual Effects–Web–Gaming, MAAC Kolkata with a view to educating the leaders about the different color wheel theories that are popular in the field of hues.